Sign Language Translation
Sign language translation is the process of converting sign language gestures into spoken or written language.
Papers and Code
Beyond a Single Reference: Training and Evaluation with Paraphrases in Sign Language Translation
Jan 29, 2026Most Sign Language Translation (SLT) corpora pair each signed utterance with a single written-language reference, despite the highly non-isomorphic relationship between sign and spoken languages, where multiple translations can be equally valid. This limitation constrains both model training and evaluation, particularly for n-gram-based metrics such as BLEU. In this work, we investigate the use of Large Language Models to automatically generate paraphrased variants of written-language translations as synthetic alternative references for SLT. First, we compare multiple paraphrasing strategies and models using an adapted ParaScore metric. Second, we study the impact of paraphrases on both training and evaluation of the pose-based T5 model on the YouTubeASL and How2Sign datasets. Our results show that naively incorporating paraphrases during training does not improve translation performance and can even be detrimental. In contrast, using paraphrases during evaluation leads to higher automatic scores and better alignment with human judgments. To formalize this observation, we introduce BLEUpara, an extension of BLEU that evaluates translations against multiple paraphrased references. Human evaluation confirms that BLEUpara correlates more strongly with perceived translation quality. We release all generated paraphrases, generation and evaluation code to support reproducible and more reliable evaluation of SLT systems.
MaDiS: Taming Masked Diffusion Language Models for Sign Language Generation
Jan 27, 2026Sign language generation (SLG) aims to translate written texts into expressive sign motions, bridging communication barriers for the Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing communities. Recent studies formulate SLG within the language modeling framework using autoregressive language models, which suffer from unidirectional context modeling and slow token-by-token inference. To address these limitations, we present MaDiS, a masked-diffusion-based language model for SLG that captures bidirectional dependencies and supports efficient parallel multi-token generation. We further introduce a tri-level cross-modal pretraining scheme that jointly learns from token-, latent-, and 3D physical-space objectives, leading to richer and more grounded sign representations. To accelerate model convergence in the fine-tuning stage, we design a novel unmasking strategy with temporal checkpoints, reducing the combinatorial complexity of unmasking orders by over $10^{41}$ times. In addition, a mixture-of-parts embedding layer is developed to effectively fuse information stored in different part-wise sign tokens through learnable gates and well-optimized codebooks. Extensive experiments on CSL-Daily, Phoenix-2014T, and How2Sign demonstrate that MaDiS achieves superior performance across multiple metrics, including DTW error and two newly introduced metrics, SiBLEU and SiCLIP, while reducing inference latency by nearly 30%. Code and models will be released on our project page.
EASLT: Emotion-Aware Sign Language Translation
Jan 07, 2026Sign Language Translation (SLT) is a complex cross-modal task requiring the integration of Manual Signals (MS) and Non-Manual Signals (NMS). While recent gloss-free SLT methods have made strides in translating manual gestures, they frequently overlook the semantic criticality of facial expressions, resulting in ambiguity when distinct concepts share identical manual articulations. To address this, we present **EASLT** (**E**motion-**A**ware **S**ign **L**anguage **T**ranslation), a framework that treats facial affect not as auxiliary information, but as a robust semantic anchor. Unlike methods that relegate facial expressions to a secondary role, EASLT incorporates a dedicated emotional encoder to capture continuous affective dynamics. These representations are integrated via a novel *Emotion-Aware Fusion* (EAF) module, which adaptively recalibrates spatio-temporal sign features based on affective context to resolve semantic ambiguities. Extensive evaluations on the PHOENIX14T and CSL-Daily benchmarks demonstrate that EASLT establishes advanced performance among gloss-free methods, achieving BLEU-4 scores of 26.15 and 22.80, and BLEURT scores of 61.0 and 57.8, respectively. Ablation studies confirm that explicitly modeling emotion effectively decouples affective semantics from manual dynamics, significantly enhancing translation fidelity. Code is available at https://github.com/TuGuobin/EASLT.
CSF: Contrastive Semantic Features for Direct Multilingual Sign Language Generation
Jan 05, 2026Sign language translation systems typically require English as an intermediary language, creating barriers for non-English speakers in the global deaf community. We present Canonical Semantic Form (CSF), a language-agnostic semantic representation framework that enables direct translation from any source language to sign language without English mediation. CSF decomposes utterances into nine universal semantic slots: event, intent, time, condition, agent, object, location, purpose, and modifier. A key contribution is our comprehensive condition taxonomy comprising 35 condition types across eight semantic categories, enabling nuanced representation of conditional expressions common in everyday communication. We train a lightweight transformer-based extractor (0.74 MB) that achieves 99.03% average slot extraction accuracy across four typologically diverse languages: English, Vietnamese, Japanese, and French. The model demonstrates particularly strong performance on condition classification (99.4% accuracy) despite the 35-class complexity. With inference latency of 3.02ms on CPU, our approach enables real-time sign language generation in browser-based applications. We release our code, trained models, and multilingual dataset to support further research in accessible sign language technology.
Lost in Translation, Found in Embeddings: Sign Language Translation and Alignment
Dec 08, 2025
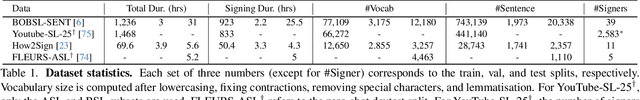
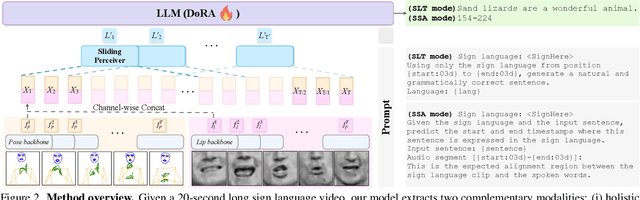
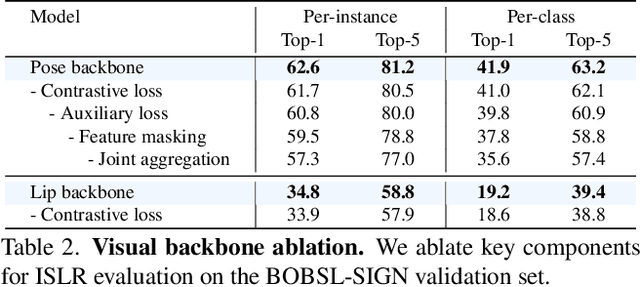
Our aim is to develop a unified model for sign language understanding, that performs sign language translation (SLT) and sign-subtitle alignment (SSA). Together, these two tasks enable the conversion of continuous signing videos into spoken language text and also the temporal alignment of signing with subtitles -- both essential for practical communication, large-scale corpus construction, and educational applications. To achieve this, our approach is built upon three components: (i) a lightweight visual backbone that captures manual and non-manual cues from human keypoints and lip-region images while preserving signer privacy; (ii) a Sliding Perceiver mapping network that aggregates consecutive visual features into word-level embeddings to bridge the vision-text gap; and (iii) a multi-task scalable training strategy that jointly optimises SLT and SSA, reinforcing both linguistic and temporal alignment. To promote cross-linguistic generalisation, we pretrain our model on large-scale sign-text corpora covering British Sign Language (BSL) and American Sign Language (ASL) from the BOBSL and YouTube-SL-25 datasets. With this multilingual pretraining and strong model design, we achieve state-of-the-art results on the challenging BOBSL (BSL) dataset for both SLT and SSA. Our model also demonstrates robust zero-shot generalisation and finetuned SLT performance on How2Sign (ASL), highlighting the potential of scalable translation across different sign languages.
RVLF: A Reinforcing Vision-Language Framework for Gloss-Free Sign Language Translation
Dec 08, 2025Gloss-free sign language translation (SLT) is hindered by two key challenges: **inadequate sign representation** that fails to capture nuanced visual cues, and **sentence-level semantic misalignment** in current LLM-based methods, which limits translation quality. To address these issues, we propose a three-stage **r**einforcing **v**ision-**l**anguage **f**ramework (**RVLF**). We build a large vision-language model (LVLM) specifically designed for sign language, and then combine it with reinforcement learning (RL) to adaptively enhance translation performance. First, for a sufficient representation of sign language, RVLF introduces an effective semantic representation learning mechanism that fuses skeleton-based motion cues with semantically rich visual features extracted via DINOv2, followed by instruction tuning to obtain a strong SLT-SFT baseline. Then, to improve sentence-level semantic misalignment, we introduce a GRPO-based optimization strategy that fine-tunes the SLT-SFT model with a reward function combining translation fidelity (BLEU) and sentence completeness (ROUGE), yielding the optimized model termed SLT-GRPO. Our conceptually simple framework yields substantial gains under the gloss-free SLT setting without pre-training on any external large-scale sign language datasets, improving BLEU-4 scores by +5.1, +1.11, +1.4, and +1.61 on the CSL-Daily, PHOENIX-2014T, How2Sign, and OpenASL datasets, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to incorporate GRPO into SLT. Extensive experiments and ablation studies validate the effectiveness of GRPO-based optimization in enhancing both translation quality and semantic consistency.
Isolated Sign Language Recognition with Segmentation and Pose Estimation
Dec 16, 2025
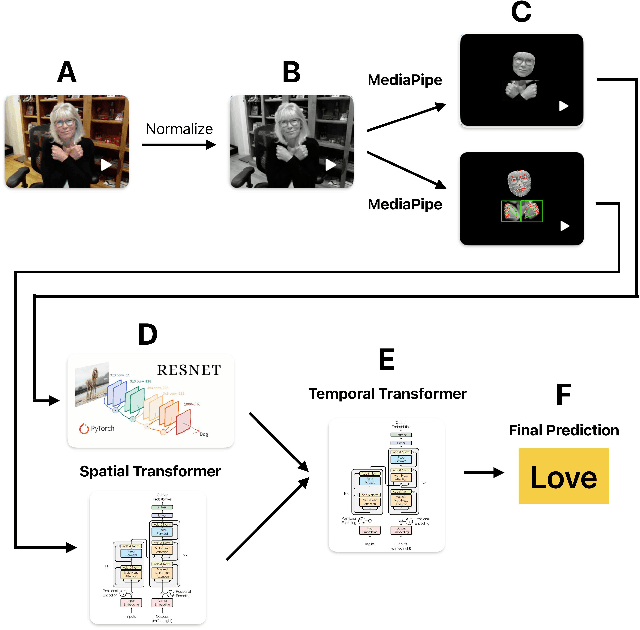
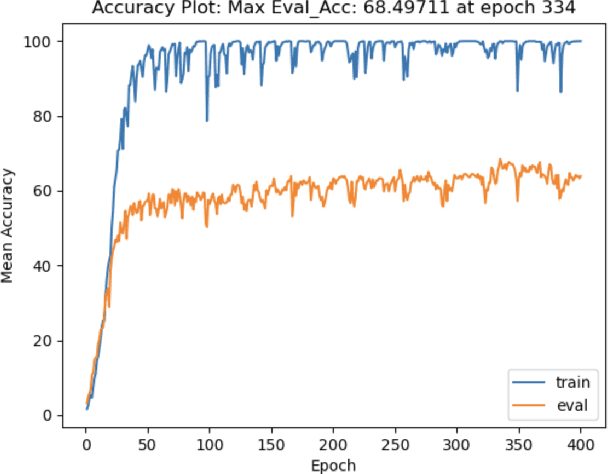
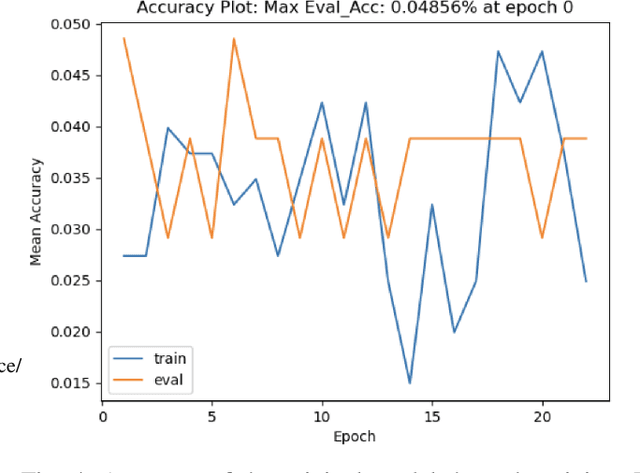
The recent surge in large language models has automated translations of spoken and written languages. However, these advances remain largely inaccessible to American Sign Language (ASL) users, whose language relies on complex visual cues. Isolated sign language recognition (ISLR) - the task of classifying videos of individual signs - can help bridge this gap but is currently limited by scarce per-sign data, high signer variability, and substantial computational costs. We propose a model for ISLR that reduces computational requirements while maintaining robustness to signer variation. Our approach integrates (i) a pose estimation pipeline to extract hand and face joint coordinates, (ii) a segmentation module that isolates relevant information, and (iii) a ResNet-Transformer backbone to jointly model spatial and temporal dependencies.
Large Sign Language Models: Toward 3D American Sign Language Translation
Nov 11, 2025We present Large Sign Language Models (LSLM), a novel framework for translating 3D American Sign Language (ASL) by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) as the backbone, which can benefit hearing-impaired individuals' virtual communication. Unlike existing sign language recognition methods that rely on 2D video, our approach directly utilizes 3D sign language data to capture rich spatial, gestural, and depth information in 3D scenes. This enables more accurate and resilient translation, enhancing digital communication accessibility for the hearing-impaired community. Beyond the task of ASL translation, our work explores the integration of complex, embodied multimodal languages into the processing capabilities of LLMs, moving beyond purely text-based inputs to broaden their understanding of human communication. We investigate both direct translation from 3D gesture features to text and an instruction-guided setting where translations can be modulated by external prompts, offering greater flexibility. This work provides a foundational step toward inclusive, multimodal intelligent systems capable of understanding diverse forms of language.
Introducing A Bangla Sentence - Gloss Pair Dataset for Bangla Sign Language Translation and Research
Nov 11, 2025Bangla Sign Language (BdSL) translation represents a low-resource NLP task due to the lack of large-scale datasets that address sentence-level translation. Correspondingly, existing research in this field has been limited to word and alphabet level detection. In this work, we introduce Bangla-SGP, a novel parallel dataset consisting of 1,000 human-annotated sentence-gloss pairs which was augmented with around 3,000 synthetically generated pairs using syntactic and morphological rules through a rule-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline. The gloss sequences of the spoken Bangla sentences are made up of individual glosses which are Bangla sign supported words and serve as an intermediate representation for a continuous sign. Our dataset consists of 1000 high quality Bangla sentences that are manually annotated into a gloss sequence by a professional signer. The augmentation process incorporates rule-based linguistic strategies and prompt engineering techniques that we have adopted by critically analyzing our human annotated sentence-gloss pairs and by working closely with our professional signer. Furthermore, we fine-tune several transformer-based models such as mBart50, Google mT5, GPT4.1-nano and evaluate their sentence-to-gloss translation performance using BLEU scores, based on these evaluation metrics we compare the model's gloss-translation consistency across our dataset and the RWTH-PHOENIX-2014T benchmark.
IsoSignVid2Aud: Sign Language Video to Audio Conversion without Text Intermediaries
Oct 09, 2025Sign language to spoken language audio translation is important to connect the hearing- and speech-challenged humans with others. We consider sign language videos with isolated sign sequences rather than continuous grammatical signing. Such videos are useful in educational applications and sign prompt interfaces. Towards this, we propose IsoSignVid2Aud, a novel end-to-end framework that translates sign language videos with a sequence of possibly non-grammatic continuous signs to speech without requiring intermediate text representation, providing immediate communication benefits while avoiding the latency and cascading errors inherent in multi-stage translation systems. Our approach combines an I3D-based feature extraction module with a specialized feature transformation network and an audio generation pipeline, utilizing a novel Non-Maximal Suppression (NMS) algorithm for the temporal detection of signs in non-grammatic continuous sequences. Experimental results demonstrate competitive performance on ASL-Citizen-1500 and WLASL-100 datasets with Top-1 accuracies of 72.01\% and 78.67\%, respectively, and audio quality metrics (PESQ: 2.67, STOI: 0.73) indicating intelligible speech output. Code is available at: https://github.com/BheeshmSharma/IsoSignVid2Aud_AIMLsystems-2025.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge